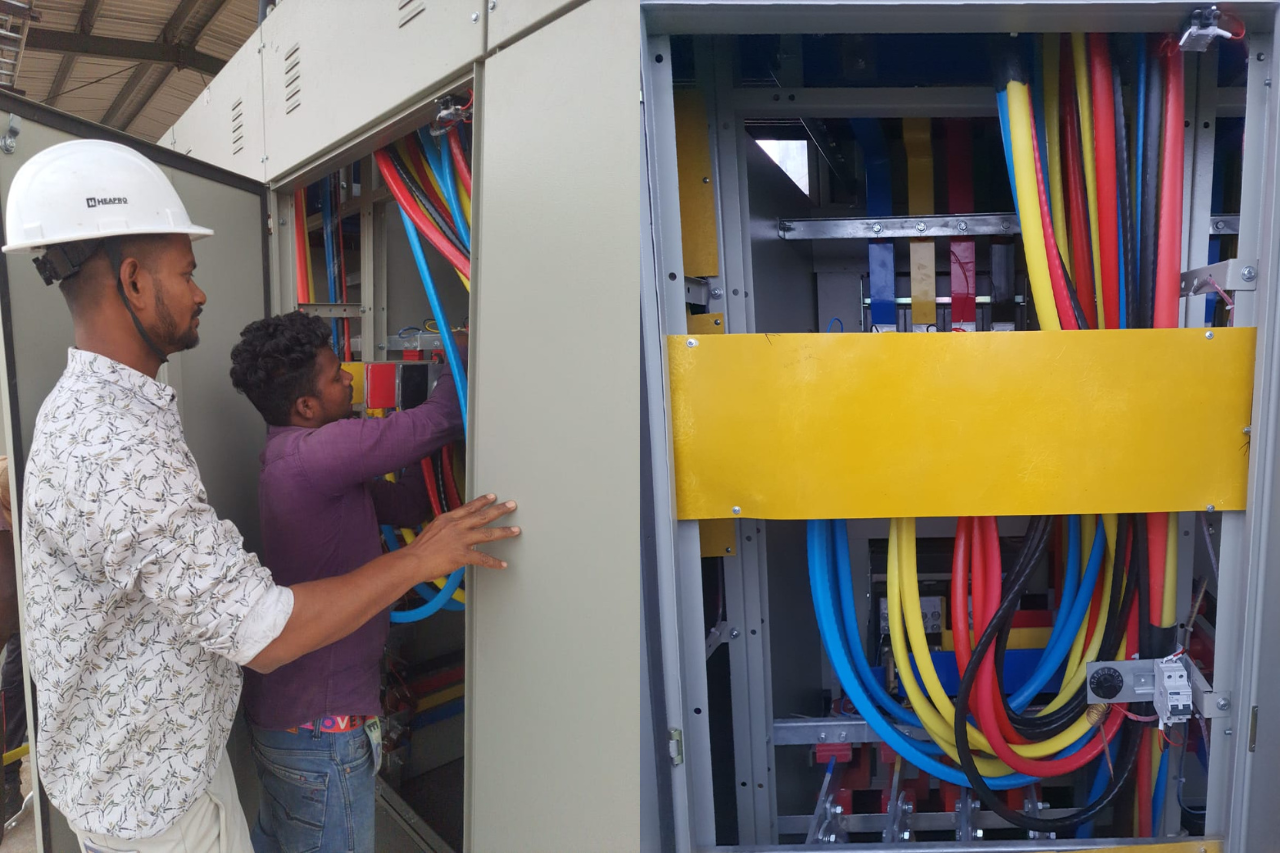
Industrial LVDS Work
Industrial LVDS Work
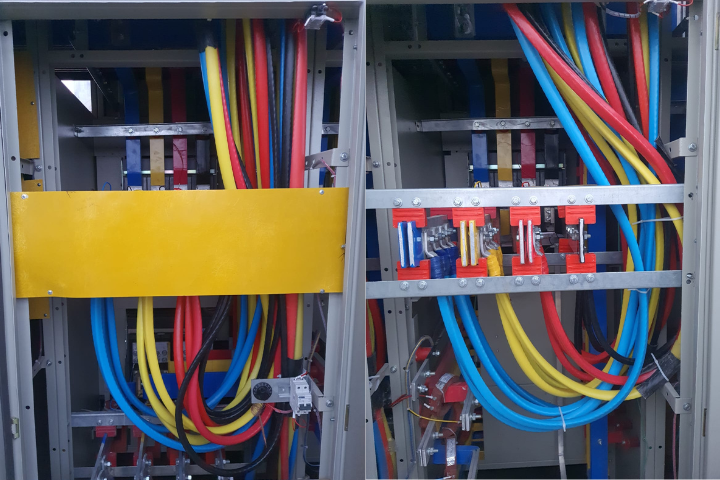
Industrial Low Voltage Distribution System (LVDS) work involves the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems that distribute low-voltage power (typically up to 1000V) to various industrial equipment and machinery. These systems are crucial for powering motors, lighting, control panels, and other essential operations within factories, plants, and industrial facilities. At Padmavatee Electrical Services, we specialize in the implementation of efficient and safe LVDS solutions, ensuring that power distribution is reliable, energy-efficient, and meets industry standards.
Our team focuses on delivering customized designs that suit specific operational requirements while minimizing downtime and ensuring system longevity. From initial design to final commissioning, we provide comprehensive services that enhance performance, safety, and operational continuity in industrial environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
An Industrial LVDS is a system used to distribute low-voltage electrical power (typically up to 1000V) within industrial facilities, such as factories, plants, or manufacturing units. It supplies power to machinery, control systems, lighting, and other critical equipment, ensuring reliable and safe operation of industrial processes.
Key components of an LVDS include transformers, distribution boards, circuit breakers, switchgear, control panels, cables, and protection devices. These elements work together to safely manage and distribute electrical power to various machines and systems within the industrial facility.
Proper design and installation are crucial for ensuring system safety, efficiency, and reliability. A well-designed LVDS minimizes the risk of electrical faults, reduces energy losses, ensures compliance with safety standards, and optimizes the performance of industrial operations by preventing equipment downtime.
Safety is ensured through the use of high-quality components, proper grounding, circuit protection (such as fuses and breakers), and careful adherence to electrical codes and standards. Regular inspections, routine maintenance, and the integration of protective relays help monitor the system and detect any potential faults early.
Common challenges include managing power loads for heavy machinery, minimizing energy loss due to long cable runs, ensuring compatibility with existing systems, and adhering to strict safety and regulatory standards. Additionally, environmental factors such as dust, heat, and humidity can affect the longevity and reliability of the system, requiring careful material selection and design.


